Stroke rehabilitation has different dimensions that should be considered.
Definition of disease:
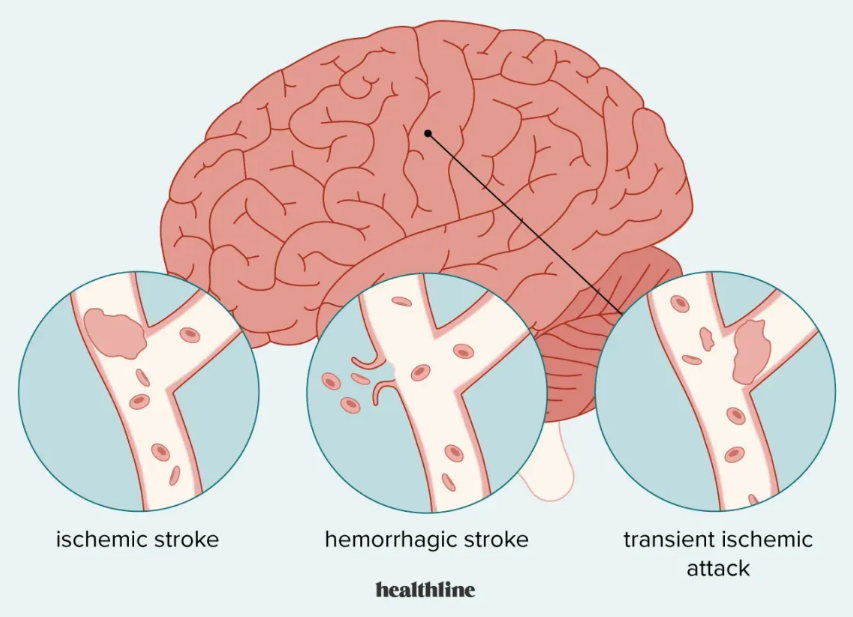
A stroke is a condition in which the blood vessels of the brain are blocked and oxygen and nutrients do not reach the sensitive tissue of the brain, and the brain cells die and fail. Sometimes, after blockage of blood vessels, bleeding also occurs in the brain tissue, which increases the patient’s problems. This disease can be associated with clinical symptoms such as inability to speak, inability to move arms and legs, confusion and cognitive problems or even decreased level of consciousness. Sometimes this vascular blockage is temporary and disappears within 24 hours, which is called TIA or transient stroke.
After hospitalization and stabilization of vital signs and acute problems of the patient, rehabilitation treatment should be started immediately. In fact, the first three months after the stroke are called the golden times, when the maximum recovery of the patient is achieved during this time.
Treatment:
Stroke rehabilitation treatment is a team work, which is often managed by physical medicine and rehabilitation specialists, and other specialists such as neurology or psychology can also be used. The rehabilitation team basically includes a physiotherapist, speech therapist, occupational therapist, and depending on the patient’s condition and needs, a respiratory therapist, a psychologist, and a social worker can be added to the team.
The main task of the physiotherapist is to focus on gross movements of the limbs and often the lower limbs, and includes helping to strengthen muscle strength and improving limb movements and balance and helping the patient to walk. The task of occupational therapy is to try to improve the fine movements of the hands and create the ability to perform daily activities including eating, dressing, cleaning and bathing independently and using tools. Speech therapy focuses on cognitive and speech abilities, as well as the patient’s ability to communicate with others and the ability to eat and drink.
Treatment places:
After discharge from acute treatment centers such as hospitals and emergency centers, the continuation of treatment can happen in three ways.
A: In patients with lower degrees of problems, treatment is done in physiotherapy centers as a daily visit, so the patient visits these centers three to five times a week and continues his treatment.
B: In other cases, the rehabilitation team goes to the patient’s home and the rehabilitation process is carried out at home. This method has limitations due to lack of access to some specialized facilities at home and should be used only when necessary.
C: In cases where the patient has more serious problems, such as the need to continue special medical treatments, or unstable conditions of vital signs, or severe loss of consciousness, or when there is a need for intensive care, inpatient rehabilitation centers are the right place to continue the treatment process. be These centers have 24-hour care by the medical staff and the rehabilitation treatment team works on the patient’s recovery in the same place.
The ultimate goal:
The final goal of rehabilitation treatment is to create maximum individual independence in the injured person to perform daily activities, occupational activities, social activities and miscellaneous activities such as sports and recreation. Of course, treatment does not happen 100% in all people, and stages of disability may always remain for the patient. In some cases, to correct the patient’s disability, it is possible to get help from external devices such as orthoses or corrective surgeries.
Written by Rehabex team